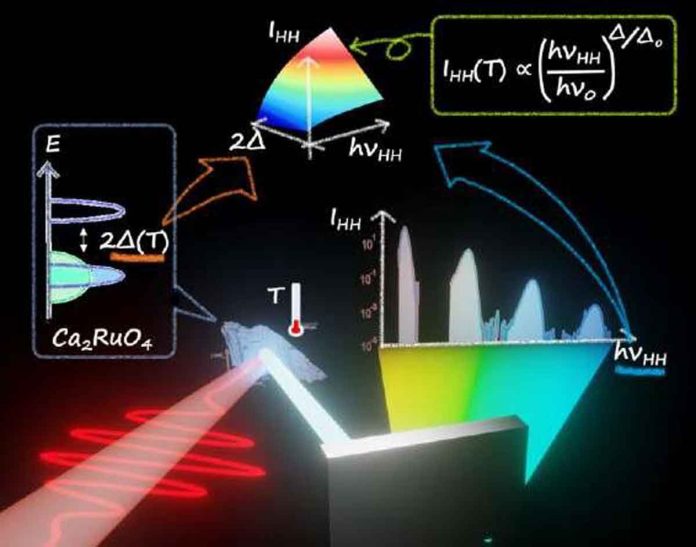
Materials scientists will soon be able to control material properties with light. Kyoto University and Kurume Institute of Technology researchers have discovered a scaling law that determines high-order harmonic generation in the solid-layered perovskite material named Ca2RuO4.
High-order harmonic generation is a nonlinear optical phenomenon. There extreme ultraviolet photons are emitted by a material as a result of interactions with high intensity light.
The characteristics of high-order harmonic generation can only be established by understanding how these electrons move in the presence of light, due to the strong interaction between electrons in these solids.
Scientists set out to observe the relationship between temperature and photon emission in Ca2RuO4, to tackle this question. They used a mid-infrared pulse to measure and map out high harmonic generation intensity at temperatures from an extremely low 50 to a moderate 290 Kelvin.
Scientists recorded high-order harmonic generation several hundred times more intense than at room temperature. Photon emissions continued to intensify with increasing gap energy. The energy required for electrons to conduct electricity with the drop in temperature.
Scientists found that such emissions occurred in the Mott-insulating phase of the material. There the strong repulsion between electrons and high gap energy transforms the metal from an electrical conductor to an insulator. This scaling law can direct theoretical studies towards more refined descriptions of non-equilibrium electron dynamics in strongly correlated materials. This is a central issue in condensed matter physics.