In a groundbreaking development, scientists at the U.S. Department of Energy’s National Renewable Energy Laboratory (NREL) have introduced a cutting-edge bifacial perovskite solar cell that has the potential to revolutionize the renewable energy landscape.
This innovative solar cell, designed to harness sunlight on both its front and back sides, is proving to be a game-changer in the industry.
Dual Nature Enhances Energy Yields
The key advantage of the bifacial perovskite solar cell lies in its dual nature, which enables it to capture direct sunlight on the front and reflected sunlight on the back.
This unique capability allows the cell to outperform its monofacial counterparts, offering significantly higher energy yields at lower overall costs.
Kai Zhu, a senior scientist at NREL’s Chemistry and Nanoscience Center, who is also the lead author of the study published in the prestigious journal Joule, explains the remarkable efficiency of the perovskite cell from either side.
He collaborated with fellow researchers, including Qi Jiang, Rosemary Bramante, Paul Ndione, Robert Tirawat, and Joseph Berry from NREL, along with other co-authors from the University of Toledo.
Bridging the Efficiency Gap
In the past, bifacial perovskite solar cell research faced challenges with efficiency, often lagging behind monofacial cells which boasted a current record of 26% efficiency.
To be truly competitive, the NREL researchers aimed to achieve front-side efficiency comparable to the best-performing monofacial cell, along with similar back-side efficiency.
Through meticulous research and experimentation, the team successfully constructed a solar cell with closely aligned efficiencies from both front and back illuminations.
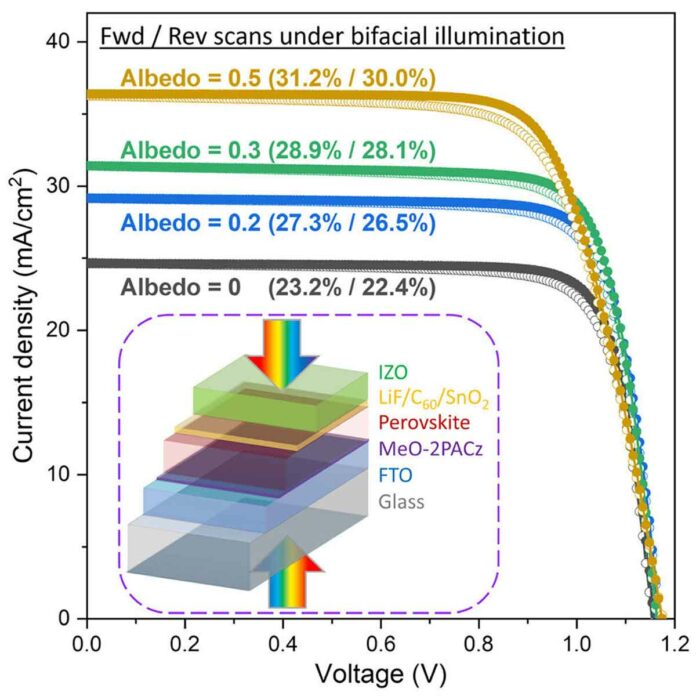
The front illumination exhibited an impressive efficiency of over 23%, while the back illumination reached approximately 91%–93% of the front’s efficiency.
Simulation-Guided Design
The development of the bifacial perovskite cell was guided by advanced optical and electrical simulations.
These simulations played a crucial role in determining the optimal thickness of the perovskite layer on both sides of the cell.
For the front side, the researchers had to find the perfect balance between absorbing most of the photons from a specific part of the solar spectrum and avoiding excessive photon blockage due to a thick perovskite layer.
On the other hand, the ideal thickness of the rear electrode on the back side needed to be identified to minimize resistive loss.
Zhu emphasizes that without the aid of simulations, producing cell after cell experimentally would have been necessary to reach the ideal thickness.
However, the team managed to find the sweet spot, with the perovskite layer’s optimal thickness measuring around 850 nanometers – a tiny fraction compared to a human hair, which is approximately 70,000 nanometers wide.
The Road to a Bright Future
To assess the efficacy of bifacial illumination, the researchers placed the solar cell between two solar simulators.
The front side received direct light, while the back side was exposed to reflected light.
As the ratio of reflected light to front illumination increased, so did the efficiency of the cell, highlighting the immense potential of this technology.
While the initial manufacturing costs of bifacial perovskite solar modules are estimated to be higher than monofacial modules, the long-term benefits are undeniable.
Researchers project that over time, bifacial modules could prove to be more financially rewarding, generating approximately 10%–20% more power.
The introduction of the bifacial perovskite solar cell marks a significant milestone in the pursuit of sustainable and efficient renewable energy solutions.
As researchers continue to refine and optimize this groundbreaking technology, the future of solar energy looks brighter than ever before.
FAQs
A bifacial perovskite solar cell is an advanced type of solar cell that can capture sunlight on both its front and back sides. Unlike traditional monofacial solar cells, which only utilize one side to absorb sunlight, the bifacial design allows for increased energy yields by taking advantage of reflected sunlight as well.
The dual nature of the bifacial perovskite solar cell enables it to gather direct sunlight from the front side while simultaneously capturing reflected sunlight from the back side. This ability significantly enhances its overall efficiency and energy production, making it more effective than traditional monofacial cells.
Perovskite materials have gained attention in solar cell research due to their exceptional light-absorbing properties and cost-effectiveness in manufacturing. They offer the potential to revolutionize the solar energy industry with their high efficiency and low production costs.
The bifacial perovskite solar cell was developed by scientists at the U.S. Department of Energy’s National Renewable Energy Laboratory (NREL). The lead author of the research paper on this breakthrough technology is Kai Zhu, a senior scientist at NREL’s Chemistry and Nanoscience Center.
The bifacial perovskite solar cell demonstrated an impressive front-side efficiency of above 23% during lab measurements. Moreover, the efficiency from the back-side illumination was approximately 91%–93% of the front-side efficiency, showcasing its high performance.
To determine the ideal thickness of the perovskite layer, researchers relied on advanced optical and electrical simulations. These simulations guided the design process, helping to strike the right balance between photon absorption and avoiding excess blockage, ultimately leading to an optimal thickness of around 850 nanometers.
To evaluate the efficiency gained through bifacial illumination, the researchers placed the solar cell between two solar simulators. The front side received direct light, while the back side received reflected light. As the ratio of reflected light to front illumination increased, the efficiency of the cell also increased, demonstrating its potential for superior performance.
Initially, bifacial perovskite solar modules might incur higher manufacturing costs compared to traditional monofacial modules. However, over time, the increased energy generation, ranging from 10%–20%, can make bifacial modules a more financially sound investment.
The bifacial perovskite solar cell’s ability to produce higher energy yields at lower costs can significantly contribute to increasing the adoption of renewable energy sources. Its efficiency and cost-effectiveness may pave the way for more sustainable and environmentally friendly power generation.
More information: Joule (2023). DOI: 10.1016/j.joule.2023.06.001