Knowledge about the structure and composition of the Earth’s crust is important for understanding the dynamics of the Earth. The presence or absence of melt or fluids plays a major role in plate tectonic processes. Most our knowledge in this area comes from geophysical surveys. The relationship between measurable geophysical parameters and the actual conditions in the Earth’s interior is often ambiguous.
LMU geophysicist Max Moorkamp has developed a new method. Data on the distribution of electrical conductivity and density in the Earth’s crust is combined and processed using a method derived from medical imaging.
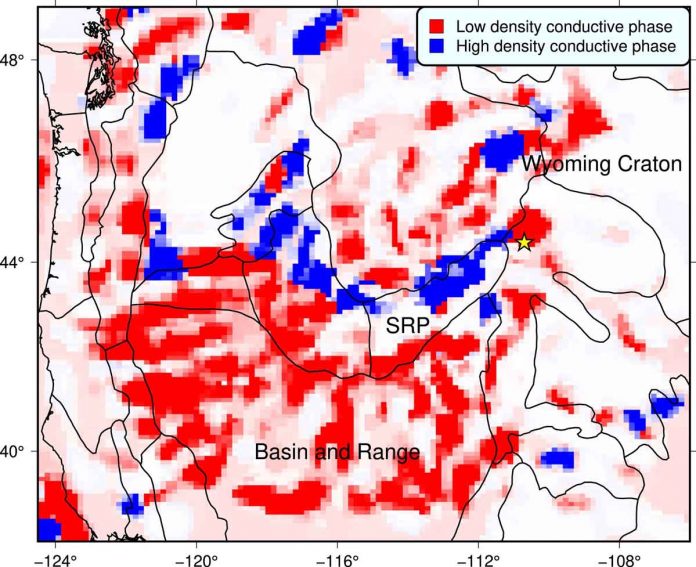
Moorkamp was able to show that previous assumptions about the spatial distribution of magma and fluids in the western United States may be overly simplified. Scientists had previously assumed that molten rock and fluids are widespread in geologically young and active regions. The electrical conductivity of molten rock and fluids is very similar to that of solid graphite and sulfides.
Moorkamp was able to distinguish between the two for the first time and so demonstrate that even in the very active region around Yellowstone. There are fluid-dominated structures directly adjacent to fluid-free areas with graphite and sulfides. The geophysicist concludes that compared to current geologic activity.
Earlier plate tectonic processes have much greater influence on the location of fluids than previously assumed. This could require a revision of previous results not only in the United States but around the globe. The technique could be very useful in the search for geothermal energy or mineral deposits.