Astronomers have stumbled upon a celestial enigma deep within the Milky Way galaxy. Dubbed “old smokers,” these peculiar stars exhibit a behavior unlike anything witnessed before.
Seemingly nearing the end of their stellar lives, they dwell quietly for extended periods, almost imperceptible, until they suddenly emit a billowing cloud of smoke.
Unveiling a Celestial Mystery
In a startling revelation, scientists have uncovered a rare breed of stars nestled within the core of our galactic home.
Termed “old smokers,” these cosmic anomalies defy conventional understanding with their elusive behavior.
Astrophysicist Philip Lucas described their actions as “peculiar” and unprecedented among red giants, shedding light on a baffling cosmic phenomenon.
Unexpected Discoveries
The revelation of these enigmatic entities arose serendipitously during a comprehensive 10-year survey of the cosmos.
While the primary focus was on identifying newborn stars, the international team of researchers stumbled upon an unexpected treasure trove of 32 proto-stars, marking a record-breaking discovery in stellar observation.
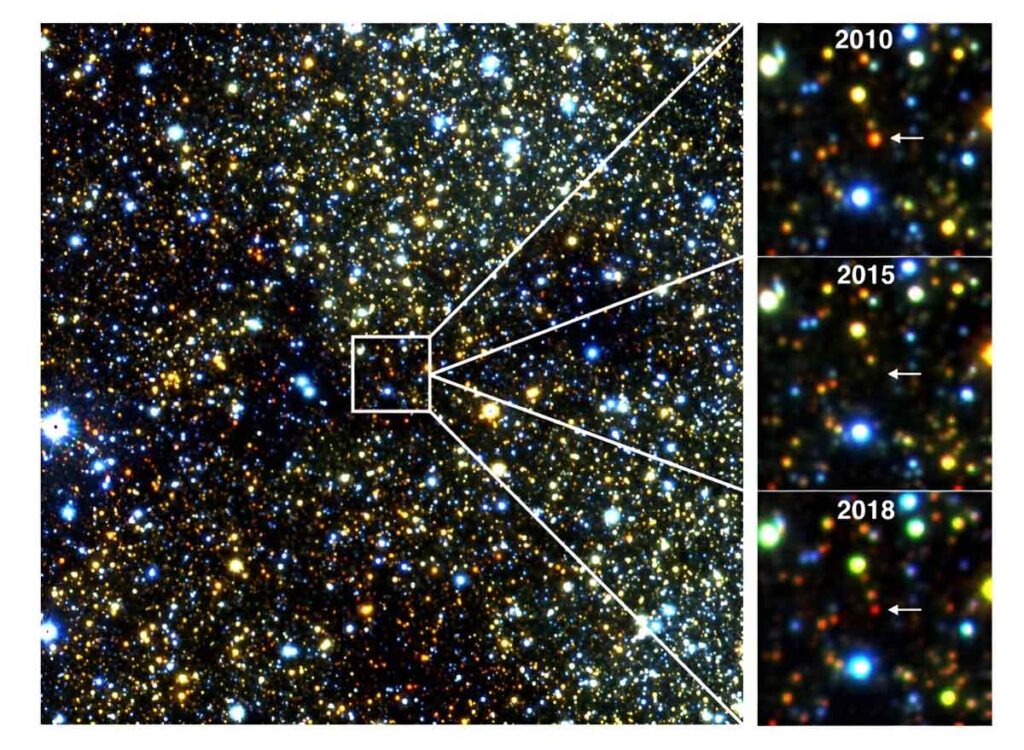
A Stellar Surprise
Amidst the hunt for nascent celestial bodies, the researchers encountered a delightful surprise lurking in the celestial depths.
Nestled within the bustling nucleus of the Milky Way, the old smokers quietly emitted their characteristic smoke rings, evoking both fascination and bewilderment among the scientific community.
The Puzzle Unfolds
The behavior of these ancient stars remains shrouded in mystery, prompting intense speculation among astronomers.
Philip Lucas remarked on the perplexing nature of their actions, suggesting a temporary obscuration of the stars’ brilliance by ephemeral smoke clouds—an intriguing hypothesis that defies easy explanation.
Unraveling the Enigma
While the exact mechanisms behind the smoke puffs elude comprehension, scientists speculate on the role of heavy elements in the process.
Within the dense environs of the Nuclear Stellar Disc, abundant in metallic compounds, these stars may harbor intricate dust formations that contribute to their enigmatic emissions.
A Cosmic Conundrum
The discovery of old smoker stars poses tantalizing questions about the dynamics of galactic evolution and the distribution of heavy elements across cosmic distances.
As researchers delve deeper into the mysteries of these celestial anomalies, the implications for our understanding of stellar phenomena and cosmic evolution continue to unfold.
Searching for Answers
Despite the myriad uncertainties surrounding their existence, astronomers remain resolute in their quest for enlightenment.
With ongoing observations and theoretical investigations, the enigma of old smoker stars may yet yield its secrets, enriching our understanding of the cosmic tapestry that envelops us.
A Stellar Revelation
The revelation of old smoker stars stands as a testament to the boundless wonders of the cosmos and the inexhaustible curiosity of the human spirit.
As we gaze upon these celestial enigmas, we are reminded of the profound mysteries that await discovery in the vast expanse of the universe.
FAQ
Old smoker stars are a newly discovered type of celestial object characterized by their unique behavior of emitting smoke-like clouds intermittently. These stars exhibit this phenomenon as they near the end of their life cycle.
Old smoker stars were discovered by a team of astronomers conducting a comprehensive survey of the Milky Way galaxy. Initially focused on identifying newborn stars, the researchers stumbled upon these enigmatic objects during their observations.
Old smoker stars have been observed in the dense and metal-rich region at the center of the Milky Way galaxy known as the Nuclear Stellar Disc. This region, teeming with stars and cosmic activity, provides an ideal environment for the study of celestial phenomena.
More information: Phil Lucas et al, The most variable VVV sources: eruptive protostars, dipping giants in the Nuclear Disc and others, Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society (2024). DOI: 10.1093/mnras/stad3929
Zhen Guo et al, Spectroscopic confirmation of high-amplitude eruptive YSOs and dipping giants from the VVV survey, Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society (2024). DOI: 10.1093/mnras/stad3700
Carlos Contreras Peña et al, On the incidence of episodic accretion in Class I YSOs from VVV, Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society (2024). DOI: 10.1093/mnras/stad3780
Zhen Guo et al, Multi-wavelength detection of an ongoing FUOr-type outburst on a low-mass YSO, Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society (2024). DOI: 10.1093/mnrasl/slad201

