The teeth of a mollusk can not only capture and chew food to nurture its body. The marine choppers also hold insights into creating advanced, lower-cost and environmentally friendly materials.
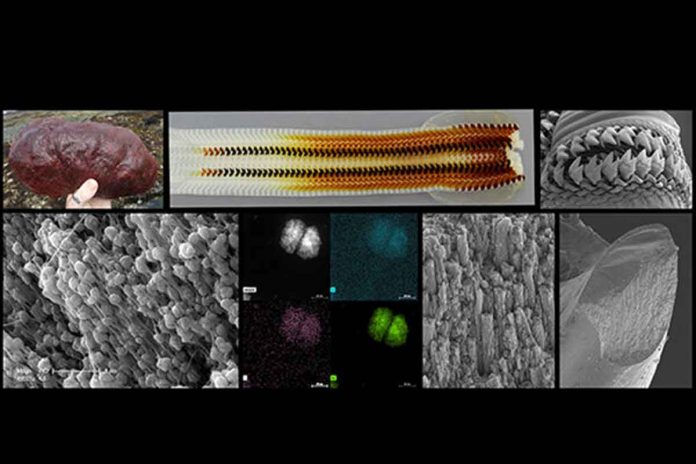
David Kisailus, UC Irvine professor and graduate student Taifeng Wang took a close look at the ultrahard teeth of the Northern Pacific Cryptochiton stelleri or gumboot chiton. The study was published in the Small Structures.
Gumboot chitons are plant-eating invertebrates. These use their ultrahard teeth to scrape and grind algal deposits from coastal rocks. Scientists found that these teeth are constructed of highly aligned magnetic nanorods. These provide strength and resistance. Scientists used nanostructural and chemical analysis of the gumboot chitons’ teeth during early-stage of maturity, to better understand how the nanorods are formed. This investigation revealed pre-assembled organic fibrous material (chitin) guided the formation of these rods via a highly ordered.
Further examination of the mesocrystalline structures uncovered a spherulitic-like architecture often found in semi-crystalline polymeric materials. Scientists determined that each of these particles had an underlying organic framework. It controls the formation and growth of these iron oxide particles.
Additional analysis showed that the ferrihydrite eventually transformed to mesocrystalline magnetite via a shear-induced phase transformation. It then grew to form the final form of continuous ultrahard magnetite nanorods in the fully mature teeth via Ostwald ripening. This is a process by which smaller particles dissolve and re-deposit to form larger particles.
These ultrahard materials are synthesized at near room temperature and under mild physiological conditions. Scientists want to understand how they are formed could provide low-cost and environmentally friendly fabrication of engineering materials with superior properties.