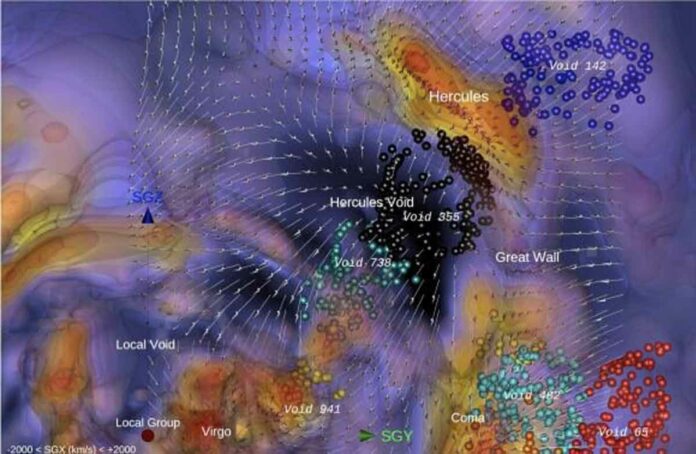
The vast empty regions known as cosmic voids dominate the universe’s large-scale structure. In the distribution of galaxies, these voids appear as holes hundreds of millions of light years across. New research indicates that many of them may still be filled with dark matter.
At the very largest scales in our universe, galaxies are not scattered around randomly like salt thrown on a table. They instead adhere to a pattern known as the cosmic web. This is the most massive pattern found in nature. The cosmic web is composed of galaxies.
The cosmic web is a network of interlocking filaments, clusters, and walls that spans the entire observable universe and beyond. The vast empty regions known as cosmic voids sit between all of those structures. These voids are 20 million light-years across at the smallest scales.
Our observations of the universe’s large-scale structure do not tell the whole story. This is because we can only see galaxies. It only makes up a small portion of the universe’s mass. The majority of the mass is made up of dark matter. Dark matter is a mysterious form of matter that does not interact with light.
Scientists have used sophisticated computer simulations to study the nature of dark matter and its relationship to normal matter. Now a team of researchers studied the seven nearest voids to the Milky Way using simulations that represent the local volume of our universe.
They discovered that, while large gaps in galaxy distributions could be identified as voids, they were not always devoid of dark matter. Half of them did not even have densities lower than the universe’s average density.
Smaller voids that form as pockets within larger structures are not completely devoid of dark matter. Whereas the largest voids are completely devoid of matter in their centres.
Understanding voids aids astronomers in their understanding of the universe’s overall structure and evolution.
More information: H. M. Courtois et al, On the sociology and hierarchy of voids: a study of seven CAVITY nearby galaxy voids and their dynamical CosmicFlows-3 environment, arXiv (2022). DOI: 10.48550/arxiv.2211.16388