Each one cells that human body have suffers nearly 10,000 DNA lesions each day. These injuries could have been catastrophic if cells were unable to repair them. But a very delicate machinery which can detects and repair genetic damage is doing its work to prevent DNA mutations and diseases such as cancer.
Researcher Bárbara Martínez of the National Cancer Research Centre together with Raul Mostoslavsky from Massachusetts General Hospital have taken the help of machine learning applied to high-throughput microscopy, among other techniques. They have visualized the DNA repair machinery in detail and identified the new repair proteins. These results have been published in Cell Reports and can help develop new cancer therapies.
Whenever there is DNA damage, like a DNA double-strand break, the cell activates a mechanism named DNA damage response. Proteins bind damaged DNA fast and send alarm signals. The signals will be recognized by other proteins that repair the damage.
Scientists said, the goal of chemotherapy is to kill tumour cells by DNA lesions. As this cause cancer cell collapse and death. Scientists have developed a new methodology that have a machine learning analysis method. This has allowed the analysis of this process with a degree of detail and precision never before achieved.
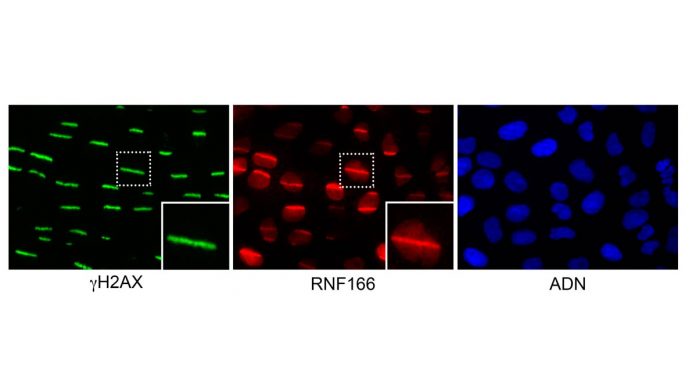
Scientists have used high-throughput microscopy that allows the acquisition of thousands of pictures of cells after induction of genetic damage. As a first step, they introduced more than 300 different proteins into the cells and evaluated in a single experiment whether they interfered with DNA repair over time. They have discovered nine new proteins that are involved in DNA repair by using this technique.
The new team of researchers have gone one step further and visually monitored 300 proteins. They have adapted a classic DNA micro-irradiation technique. This damages DNA with a UV laser. This is used on a large-scale format for the first time and analyse the behaviour of the 300 proteins studied.
One of the discovered proteins is PHF20. Scientists showed that this protein moves away from lesions within seconds after damage to facilitate the recruitment of 53BP1, which is a protein critical in DNA repair. Cells that do not have PHF20 cannot repair their DNA properly. These cells are also more sensitive to irradiation than normal cells. This means PHF20 is important for DNA repair.