Atmospheric water vapor and energy transport play a significant role in the Arctic climate. Changes in atmospheric energy and water vapor influx to the Arctic would have an important impact on the interannual variations and long-term trend of sea ice through a variety of mechanisms.
Prof. Huang Haijun from the Institute of Oceanology of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (IOCAS) have given us new insights into the impact of atmospheric moisture and energy transport on sea ice loss. The study was published in The Cryosphere.
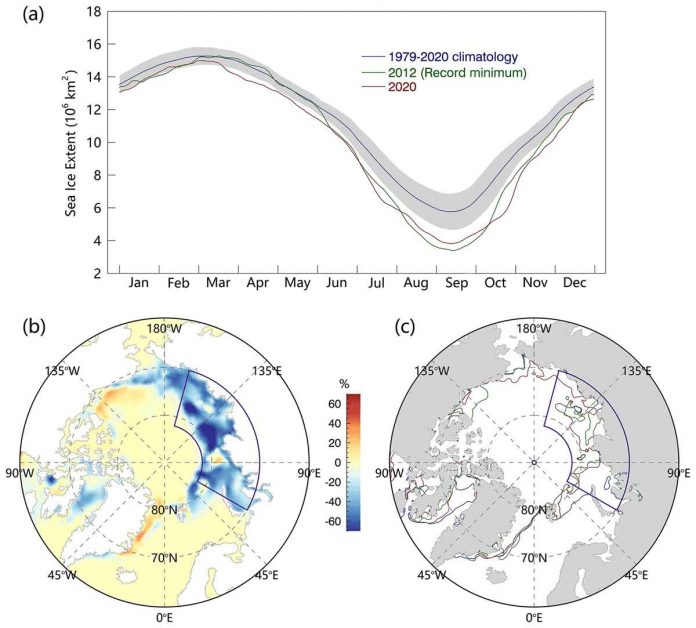
Satellite observations showed an unprecedented reduction in sea ice extent (SIE). It was observed in July 2020 in the Eurasia shelf seas including the Kara, Laptev and East Siberian Seas.
Scientists suggested that anomalously high advection of energy and water vapor prevailed during spring 2020 over the regions where conspicuous sea ice retreat occurred in the following July. They sated this based on reanalysis and modeled sea ice thickness.
The convergence of the transport increased the temperature and humidity of the atmosphere of the local area. The enhanced greenhouse effect led to strengthened downward longwave radiation plus turbulent fluxes at the surface. It initiated the earlier melt onset of sea ice in the study area. The enhanced net solar radiation absorbed by the ocean-ice system produced an accelerated decline in SIE through the ice-albedo feedback, after the melt commenced.