The East China Sea (ECS) is affected by severe hypoxia. It exerts significant influences on living resources, alterations of biogeochemical cycles and ecosystem degradation.
Previous studies have proved that organic matters (OM) decomposition in the Kuroshio Subsurface Water (KSSW) played a significant role in forming the coastal hypoxia.
Institute of Oceanology of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (IOCAS) scientists provided new information on the sources of decomposed organic matters in Kuroshio Subsurface Water on hypoxia formation in ECS by applying the nitrate isotopes technique.
The study was published in Marine Pollution Bulletin.
Scientists found stronger oxidations
Scientists found stronger oxidations in the Kuroshio Subsurface Water than ambient waters in either June or October on the ECS shelf. It reduced the dissolved oxygen in the bottom. The reaction was stronger in June than that in October.
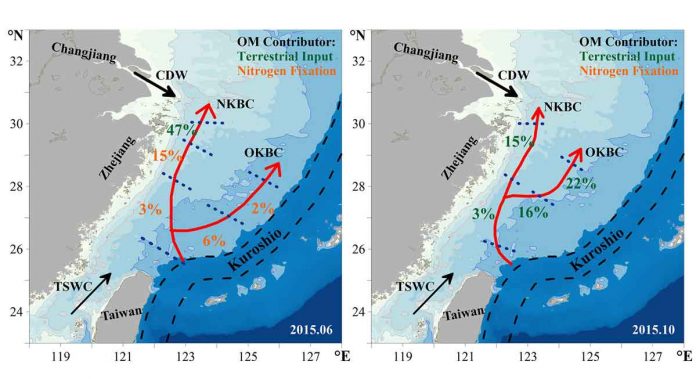
The nitrogen from N2 fixation was introduced into the bottom nitrate in Kuroshio Subsurface Water in the southern ECS during June. Those signals were hardly observed during October. The decomposition of terrestrial organic matters enhanced in the northern ECS during June and most of the ECS during October.
The decomposition of terrestrial organic matters enhanced in the northern ECS during June and most of the ECS during October., based on the isotopic balance equation. The terrestrial and marine sources contributed almost equally to the development of ECS hypoxia. This judged the impact of human activities and natural process on coastal hypoxia quantitatively.