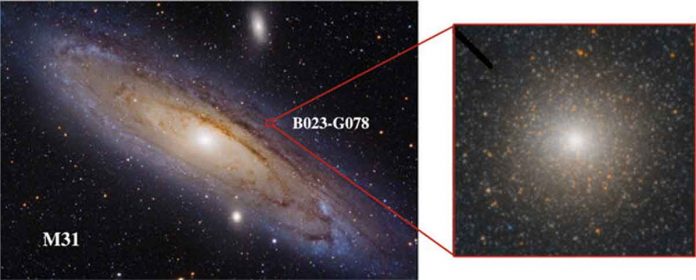
Astronomers have discovered a black hole which is smaller than the black holes we have found at the centres of galaxies. But it is bigger than the black holes that are born when stars explode. Scientists think it is one of the only confirmed intermediate-mass black holes. This is an object that has long been sought by astronomers.
The black hole was hidden within B023-G078. B023-G078 is an enormous star cluster in our closest neighbouring galaxy Andromeda. Astronomers thought it was a globular star cluster. But now scientists think it is a stripped nucleus.
Scientists explained stripped nucleus
Stripped nuclei are remnants of small galaxies. These galaxies fell into bigger ones and had their outer stars stripped away by gravitational forces. It left behind a tiny and dense nucleus orbiting the bigger galaxy and at the centre of that nucleus which is a black hole.
The research paper has been published in The Astrophysical Journal.
A decades-long hunch
B023-G078 is a massive globular star cluster. It is a spherical collection of stars bound tightly by gravity. There was only a single observation of the object that determined its overall mass. It is 6.2 million solar masses. Scientists felt it is something else.
Astronomers studied the data from the Gemini Observatory and images from the Hubble Space Telescope. Astronomers calculated how mass was distributed within the object by modelling its light profile. Astronomers explained, a globular cluster has a signature light profile. It has the same shape near the centre as it does in the outer regions. But B023-G078 is different. The light at its centre is round. Then it gets flatter moving outwards. The chemical makeup of the stars changes. There are more heavy elements in the stars at the center than those near the object’s edge.
Scientists used object’s mass distribution to predict how fast the stars should be moving at any given location within the cluster. Then they compared it to their data. They found out the highest velocity stars were orbiting around the center. Scientists built a model without including a black hole. They found the stars at the center were too slow compared their observations. Then they added the black hole. They got speeds that matched the data. The conclusion is the black hole suggests the object is a stripped nucleus.
Scientists are hoping to observe more stripped nuclei. They may hold more intermediate mass black holes. It is an opportunity to learn more about the black hole population at the centers of low-mass galaxies. Scientists will also learn about how galaxies are built up from smaller building blocks.