Daegu Gyeongbuk Institute of Science and Technology (DGIST) in Korea scientists have fabricated a flexible material that lights up brightly when stretched and/or when an electric field is applied. The study was published in the journal Applied Physics Reviews. Scientists showed promise for the development of bright, sustainable, stretchable devices for use.
Soft and light-emitting ACEL devices is made by sandwiching a light-emitting compound between two electrode layers. It needs at least one of the electrode layers to be transparent, but for the light in the middle to reach the surface and actually be seen. This leads to several issues depending on the type of material used. This includes the electrode being brittle or difficult to fabricate.
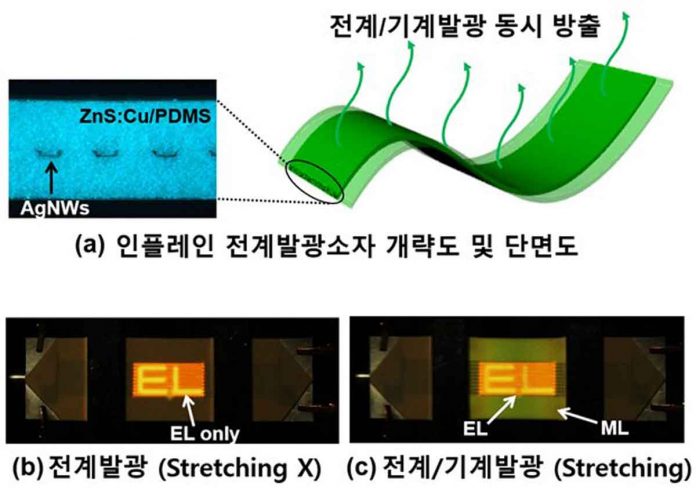
Jeong and his colleagues overcame this and other design issues in ACEL devices by inserting stretchable silver nanowire electrodes in-parallel in between two light-emitting layers made of copper-ion-doped zinc sulfide particles embedded in polydimethylsiloxane. ZnS:Cu/PDMS has an attractive property. It generates light when it is deformed. This is called mechanoluminescence. The device also becomes electroluminescent, by adding the silver nanowire electrodes. Applying an electric field to it causes the material to shine brightly.
The design also allows the use of thick light-emitting layers in contrast to previous ACEL devices that can only use layers that are thin enough to apply a strong electric field between the two electrodes. The new design overcomes this issue by inserting the electrodes as ultra-thin wires inside of the light-emitting material. The thicker material produces 3.8 times as much electroluminescent brightness as other ACEL devices.
Scientists wants to improve the device’s electroluminescence in response to a low electric field. They plan to arrange the silver nanowires in diverse directions.